■ 試験デザイン
By use of a shared decision-making recruitment strategy targeting the entire at-risk population within an integrated community healthcare system, we screened 1,808 adults meeting inclusion criteria (age 25-64, with type 2 diabetes and a BMI 30-45 kg/m(2)). Of these, 43 were allocated via concealed, computer-generated random assignment in a 1:1 ratio to RYGB or ILMI.
The primary outcome was diabetes remission at 1 year (HbA1c <6.0% [<42.1 mmol/mol], off all diabetes medicines).
TPECOに分けると下記のようになります
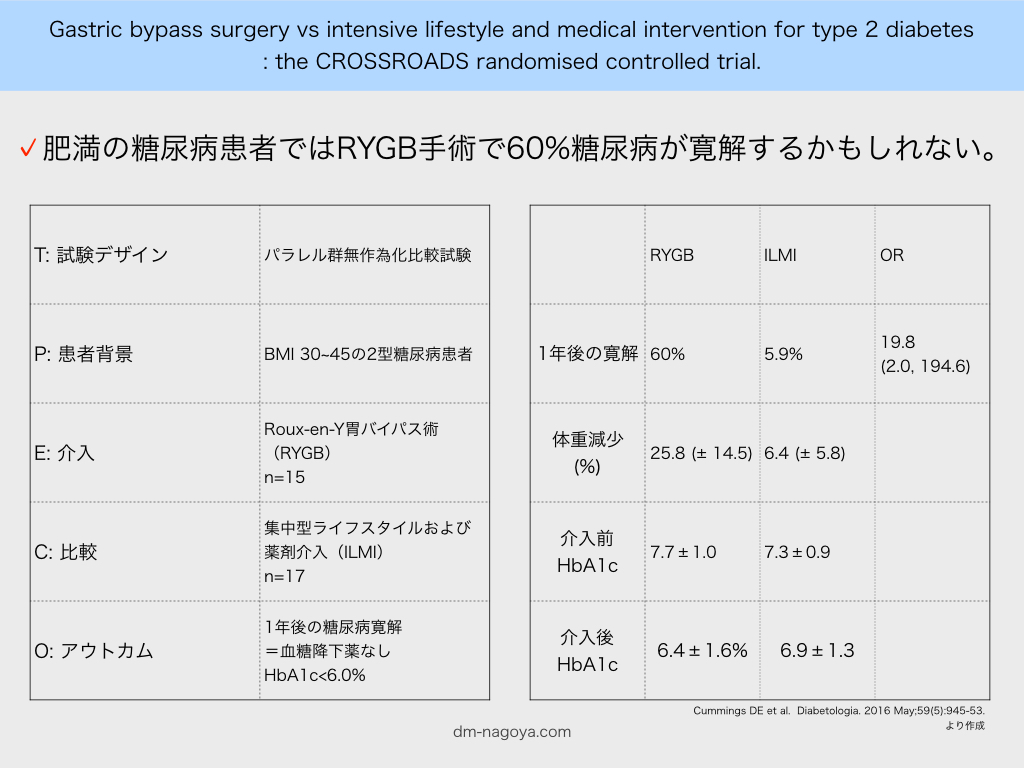
T パラレル群無作為化比較試験
P BMI 30~45の2型糖尿病患者
E Roux-en-Y胃バイパス術(RYGB) n=15
C 集中型ライフスタイルおよび薬剤介入(ILMI) n=17
O 1年後の糖尿病寛解=血糖降下薬なしでHbA1c<6.0%
■ 結果
Diabetes remission at 1 year was 60.0% with RYGB vs 5.9% with ILMI (p = 0.002). The HbA1c decline over 1 year was only modestly more after RYGB than ILMI: from 7.7 ± 1.0% (60.7 mmol/mol) to 6.4 ± 1.6% (46.4 mmol/mol) vs 7.3 ± 0.9% (56.3 mmol/mol) to 6.9 ± 1.3% (51.9 mmol/mol), respectively (p = 0.04); however, this drop occurred with significantly fewer or no diabetes medications after RYGB.
■ 副作用
No life-threatening complications occurred.
手術か否かをRCTで行うという日本では少し考えられない論文ですね。
やっぱり参加人数はかなり絞られていて、1808名にアプローチして、最終的に参加したのは32名となっております。それでもRYGBの手術をすると60%が糖尿病内服薬なしで、HbA1c6.0%未満になるという桁違いの効果をあげています(介入前は7.3~7.7%)。
文献2によると、Roux-en-Y胃バイパス術の30日死亡率は0.3%で、4.3%に1つ以上の重大有害事象が出現していたようです。
Bariatric Surgeryの論文ではしばしば死亡率は少ないと表現されるのですが、333人に1名は30日以内に死亡する加療が死亡率低いと表現されていることには違和感を覚えます。
もっともこの治療効果による長期的な予後が著しく改善したり、本人の強い希望があれば考慮はしてもよいかもしれませんが、個人的にはまだおっかないなという印象です。
■ 参照文献
文献1 Cummings DE et al., Diabetologia. 2016 May;59(5):945-53. PMID: 26983924
文献2 Longitudinal Assessment of Bariatric Surgery (LABS) Consortium et al., N Engl J Med. 2009 Jul 30;361(5):445-54. PMID: 19641201